Note¶
Note allows note values to be used for modulation.
amount sets the modulation depth.
mode selects what note value is used as modulation: pitch, dBFS, pulse or unison.
range sets the range/polarity: normal or invert.
When the note modulator is used to modulate audio effect parameters in devices placed after audio effects that mix channels (such as panners) the behaviour is as follows:
pitch: the average frequency of all notes is used.
dBFS: the average dBFS of all notes is used.
pulse: a value of 0 is used (no modulation), or the mode can’t be selected at all.
unison: the first value is used, or the mode can’t be selected at all.
Pitch¶
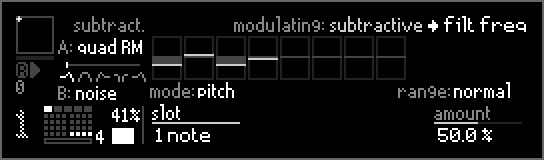
In pitch mode playing a higher note will result in a higher modulation value.
Tip
When modulating frequency parameters set amount to 50% to get 1:1 keytracking. For example: when modulating the filter cutoff and a note is played one octave higher, the filter cutoff is also adjusted to be one octave higher.
dBFS¶
In dBFS mode the loudness of notes can be mapped to modulation values.
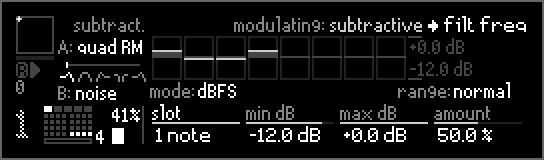
min dB sets the loudness level that maps to in fully negative modulation.
max dB sets the loudness level that results in fully positive modulation.
Pulse¶
In pulse mode a different modulation value can be set each of the four sequencer pulses.
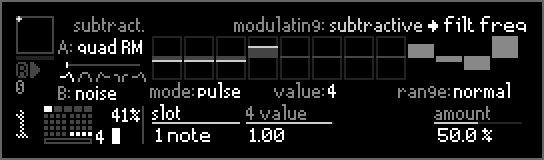
x value sets the value of the currently selected pulse.
value selects the pulse whose value can be edited using x value.
Unison¶
In unison mode a different modulation value can be set for each unison voice or channel.
Tip
Stereo signals are considered 2 voices of unison so in audio effects a different value can be set for the left channel (1 value) and the right channel (2 value).
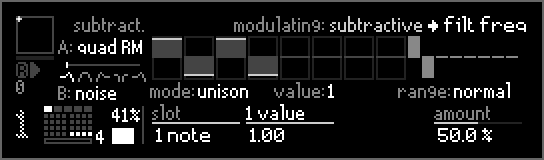
x value sets the value of the currently selected unison voice or channel.
value selects the pulse whose value can be edited using x value.